AI and SBRT: strong allies for effective treatment for lung cancer
Lung cancer is the second most common cancer worldwide. It is the most common cancer in men and the second most common cancer in women. There were more than 2.2 million new cases of lung cancer in 2021.
Until recently, conventionally fractionated high-dose radiation therapy was the preferred treatment in patients with early-stage lung cancer (e.g. non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)) who were unfit to undergo or declined surgery. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) has become an increasingly recognised treatment option for patients with inoperable peripheral early-stage lung cancer that has shown high rates of local control in prospective and retrospective series [1].
What is SBRT?
Stereotactic radiotherapy is a high-precision irradiation technique that delivers extremely precise, very intense doses of radiation to cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. The treatment is usually performed in 1 to 5 sessions (instead of the conventional 20-30 sessions) of 15 to 60 minutes.
The struggle?
SBRT has been largely deployed in cancer practices in the last decade. It has been at the core of many clinical trials that have shown SBRT to be effective at delaying disease progression and reducing recurrences. Many published reports conclude on a similar overall survival for early stages lung cancers, comparing patients who had undergone surgery and patients treated with SBRT [2,3].
Organs at risk (OARs) delineation is an essential and critical step for lung SBRT treatment planning. Manual delineation from physicians or medical physicists is nowadays the current standard of practice but it is a tedious and time-consuming process, prone to errors due to intra- and inter-observer variations.
To standardize SBRT practices, the SABR Consortium has published in 2019 a guideline to be followed for centers using the technique, setting up standards and recommendations throughout the treatment process.
How can we help?
TheraPanacea has released in 2019 an AI-powered tool for automatic delineation of OARs and lymph nodes for all anatomies. Following the SABR Consortium guidelines for SBRT delineation, Annotate by ART-Plan™ now offers new perspectives towards a fully automatic delineation of OARs for SBRT practice. The model includes all OARs needed for a SBRT protocol of central structures (trachea, proximal bronchial tree, esophagus, heart, and spinal cord), the brachial plexus and other OARs (such as stomach, bowel, liver, and spleen). The image below displays an example of the lung CT model following the SABR consortium guideline.
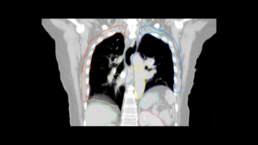
Recently, TheraPanacea has conducted a multi-centric evaluation for its Thorax SBRT model, in which manual and automated delineation using ART-PlanTM’s module Annotate were compared. The overall acceptability of the AI-model was found to be equal or superior to inter-expert variability [4].
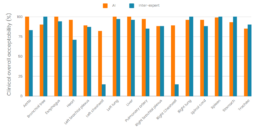
The results demonstrated that Annotate provides highly acceptable contours for all organs and can be a great ally to accelerate and standardize the SBRT clinical workflow.
Would you like to learn more?
References
[1] Murray L, Ramasamy S, Lilley J, Snee M, Clarke K, Musunuru HB, Needham A, Turner R, Sangha V, Flatley M, Franks K. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) in Patients with Medically Inoperable Peripheral Early Stage Lung Cancer: Outcomes for the First UK SABR Cohort. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2016 Jan;28(1):4-12. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2015.09.007. Epub 2015 Oct 21. PMID: 26474546.
[2] Varlotto J, Fakiris A, Flickinger J, et al. Matched-pair and propensity score comparisons of outcomes of patients with clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer treated with resection or stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer 2013;119:2683-91
[3] Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: can SBRT be comparable to surgery? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2011;81:1352-8.
[4] S. Stathakis, G. Pissakas, A. Alexiou, B. Bertrand, P.Y. Bondiau, L. Claude, T. Cuthbert, A. Damatopoulou, C. Dejean, C. Doukakis, G. Güngör, L. Hardy, E. Maani, I. Martel-Lafay, P. Mavroidis, N. Paragios, V. Peppa, D. Remonde, J.W. Shumway, G. Ugurluer, E. Ozyar. Evaluation of AI vs. Clinical Experts SBRT-Thorax Computed Tomography OARs Delineation. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics, Volume 114, Issue 3, Supplement, 2022, Pages e102-e103, ISSN 0360-3016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.07.897
Related Posts
25 June 2024
Unlocking the Potential of AI Auto-Contouring in Radiotherapy at HELSE Bergen [WEBINAR]
Clinically Relevant AI in Radiation…
24 October 2023
Innovations in Radiation Oncology: Harnessing AI for better patients outcomes [WEBINAR]
Clinically Relevant AI in Radiation…




